What are Friendly URLs? A Guide to Optimizing SEO-Friendly URLs
What are Friendly URLs?
In today’s digital world, every website wants to stand out on search engines like Google, Bing, or Yahoo. To achieve this, search engine optimization (SEO) becomes extremely important.
In addition to using meta tags effectively, one of the often overlooked but crucial factors for optimizing SEO is the use of “Friendly URLs.” So, what are Friendly URLs, and why are they so important?
Definition of Friendly URLs
Friendly URLs are web addresses designed to be easy to read and understand by both humans and machines. They usually include keywords related to the content of the page and are organized in a logical way, helping users and search engines easily understand the content of the page just by looking at the URL.

Why are Friendly URLs Important?
- Improves search engine indexing: Friendly URLs with keywords and clear structure make it easier for search engines to classify and understand the page content, thus improving visibility in search results.
- Enhances user experience: Easy-to-read and memorable URLs make it easier for users to revisit the website. This not only improves UX but also reduces bounce rates and increases time on site.
- Supports content strategy: URLs containing keywords not only optimize SEO but also support your content strategy by highlighting key topics you want users to focus on.
The Difference Between Friendly URLs and Non-Friendly URLs
- Friendly URLs are usually short, readable, and include keywords describing the content of the page.
Example: https://example.com/tips-for-seo-success - Non-Friendly URLs often contain unnecessary characters like IDs, parameters, or special characters, making them hard to read and remember.
Example: https://example.com/index.php?page=123
Switching from Non-Friendly URLs to Friendly URLs not only improves SEO but also provides a better user experience, contributing significantly to the overall success of the website.
General Rules for a Friendly URL
Choose Keywords Effectively:
- Select keywords: Choose and include keywords closely related to the page content in the URL. This increases the chances of appearing in search results for specific queries.
- Optimize length: A short and memorable URL is convenient for users and search engines, so while optimizing, it’s important to focus not only on keywords but also on URL length.
Use Hyphens to Separate Words:
Separate words: Use hyphens (-) instead of underscores (_) to separate words in the URL. Search engines like Google treat hyphens as spaces, making it easier to differentiate individual words.
Avoid Special Characters and Encoding:
Keep it simple: Avoid using special characters or encoding (such as %20 for spaces) in the URL. This not only makes the URL messy but also difficult for both users and search engines to understand.
Have a Clear Hierarchical Structure:
- Organize content: Use hierarchical structure in the URL to reflect the content structure of the website. This helps users and search engines easily understand how the content is organized.
- Clarity and consistency: Ensure each part of the URL makes sense and maintain consistency in URL structure across the website.
Guide to Optimizing SEO-Friendly URLs
Switch HTTP to HTTPS
Using HTTPS has significant SEO benefits for the following reasons:
- Google has confirmed that HTTPS is a ranking factor in their algorithm. They have also shared research showing that websites with SSL certificates tend to perform better in search results.
- Modern browsers often show security warnings when users visit websites not using HTTPS, which can negatively impact user experience and website credibility. Using HTTPS avoids this, creating a positive impression with users and increasing the click-through rate from search results since users tend to prioritize secure websites.

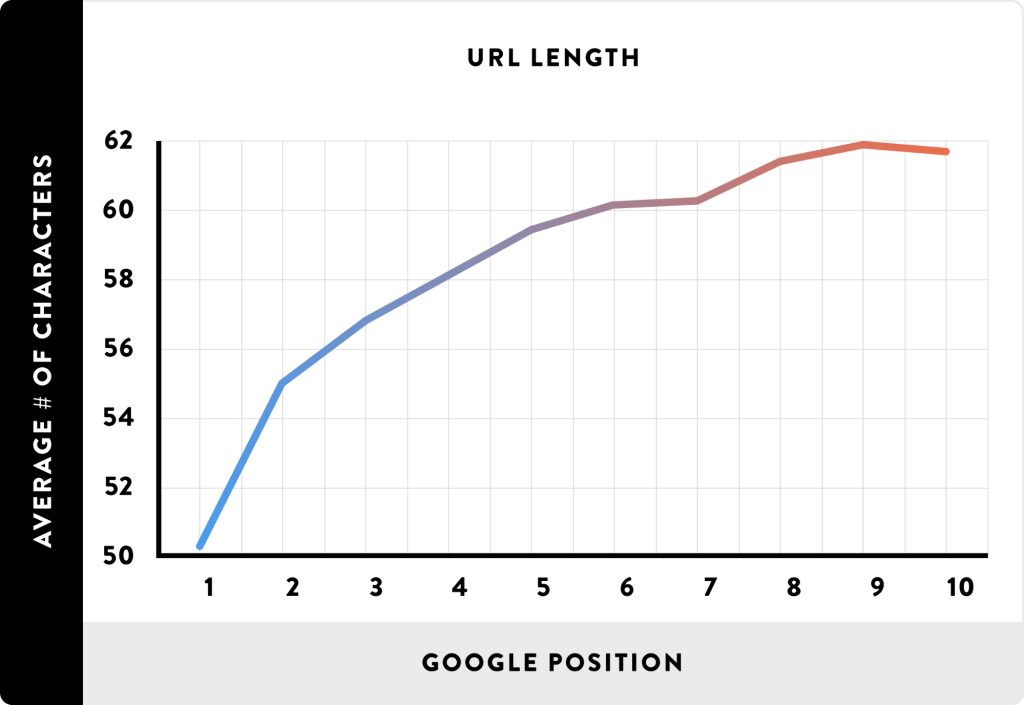
Ideal URL Length
Google does not use URL length as a ranking factor. However, shorter URLs (ranging from 50 to 60 characters) not only make the URL more readable but also ensure that the URL is not truncated in search results, allowing users to better understand the page content before clicking. This also helps googlebot crawl and index the page more efficiently and faster.
To prove this, here’s a chart showing the correlation between Google Position and URL Length:
Avoid Using Stop Words
This has been a highly debated topic: Should you use stop words or not?
What are stop words?
In SEO, “stop words” are common words in natural language like “and”, “or”, “but”, “the”, “a”, “an”, “in”, and “on”, as well as other words with little or no value for search.
Search engines typically ignore or do not consider these “stop words” when analyzing a page’s content to determine if it’s relevant to search queries. This helps optimize the search process and reduces the impact of indexing irrelevant words.
However, in some cases, stop words may still be valuable and used in SEO content for specific situations.
Reasons for Removing Stop Words:
- Optimize URL length: Make it shorter and easier to remember. This is especially useful when you want to create user-friendly URLs that are easy to share.
- Focus on keywords: Omitting stop words can help highlight important keywords, improving clarity of the page content for both users and search engines.
When to Keep Stop Words:
- Readability and context: In some cases, including stop words can make the URL easier to read and understand. For example, omitting stop words might make a URL harder to interpret or unclear in context.
- Minimal impact on SEO: Although search engines may have previously ignored stop words, they are now much smarter at understanding context and meaning. Therefore, including or omitting stop words may not significantly affect a page’s SEO position.
Therefore, if your URL structure still makes sense and is visually appealing, using stop words may only make it longer and more complex. However, if you think a stop word adds clarity and makes the URL more understandable, feel free to keep it.
Each URL Should Contain No More Than Two Directories
Using no more than two directories (or levels) for each URL is a recommended URL design principle to optimize for SEO. The goal is to keep the URL structure of the website simple, clear, and manageable.
Example:
- Multiple directory levels: http://example.com/products/electronics/mobile-phones/smartphones/
- Optimized URL: http://example.com/electronics/smartphones/
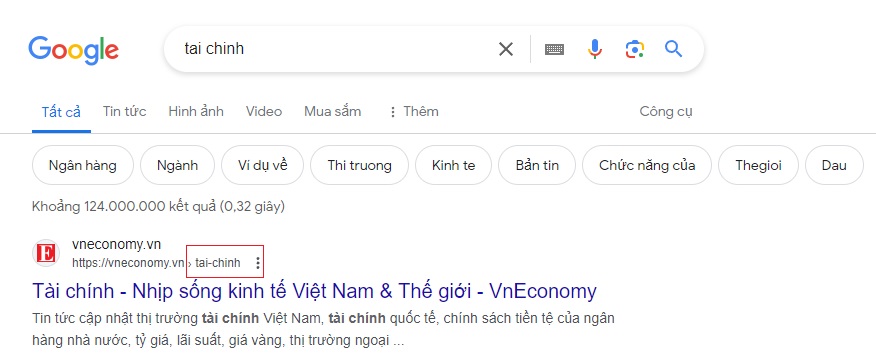
Include SEO Keywords in the URL
Including keywords in the URL is an important part of SEO optimization because it helps improve the visibility of the webpage in search engines for relevant queries. See image:
However, there are some guidelines to follow when adding keywords to the URL:
- Keyword quantity: There is no hard rule on how many keywords to include, but it is important to keep the URL concise and short. One or two main keywords are ideal, as long as they are sufficient to describe the page content and are easily searchable by users.
- Avoid keyword stuffing: Avoid overstuffing the URL with keywords (i.e., adding too many keywords unnaturally), as this not only doesn’t improve SEO but can also lead to penalties from search engines. The URL should naturally describe the content of the page.
Use Static URLs Instead of Dynamic URLs
The nature of dynamic URLs is frequent changes behind the scenes, e.g., “?id=…”. Moreover, these characters are not good for both users and Google. That’s why Google prefers static websites over dynamic ones (?id=…).

Do Not Change URLs After Google Has Indexed Them
Changing a URL after it has been indexed by Google can affect SEO and page performance on search engines. If you want to modify the content or make almost complete changes, create a new URL and 301 redirect the old URL.

Avoid Keyword Duplication
This is a small final detail.
Never repeat your keywords (or any words, for that matter) in a URL as shown in the example below from Moz.
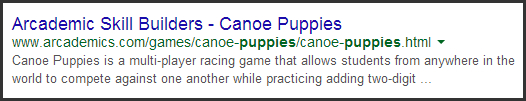
Unnaturally repeating keywords makes the URL cluttered and unprofessional. This negatively impacts the user experience and reduces the website’s credibility in the eyes of search engines.
Instead, focus on creating FRIENDLY URLs: short, clear, and naturally using keywords that accurately describe the page content.
Conclusion
Using Friendly URLs is not only good for SEO but also a crucial element in creating a high-quality user experience. Search engines are becoming smarter, but using understandable URLs containing keywords remains a strategy that cannot be ignored.
By optimizing your URLs, you help your website get found and indexed more easily by search engines, while also creating a better user experience, increasing click-through rates, and ultimately improving business performance.
 | Vương Toàn PHP Developer |